Services
Laparoscopic Splenectomy
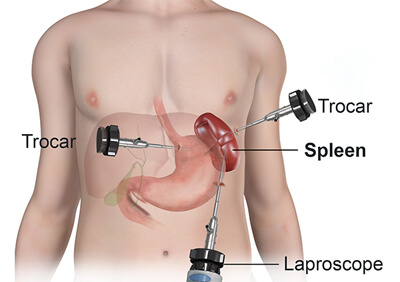
This surgery removes the spleen using small cuts in the belly. It’s a gentle, less invasive way to treat problems with the spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of your belly that helps filter blood and fight infections.
Indications for Surgery:
Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly): Often caused by infections, liver problems, or blood diseases.
Spleen Tumors: Non-cancerous or cancerous growths in the spleen.
Injury to the Spleen: When the spleen is badly hurt and can’t heal on its own.
Blood Disorders: Like ITP (Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura), where the spleen removes too many blood cells.
Procedure:
Anesthesia: You’ll be asleep and won’t feel anything during the surgery.
Small Cuts: The surgeon makes 3–4 small cuts in your belly.
Camera Inserted: A tiny camera (laparoscope) is used to see inside your belly on a screen.
Special Tools Used: Thin instruments go in through the other cuts to do the surgery.
Removing the Spleen: The surgeon carefully removes the spleen and takes it out through one of the cuts, usually inside a special bag to keep it safe.
Closing the Cuts: The small cuts are closed with stitches or glue.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Colorectal Resection:
Smaller Cuts: Less pain, smaller scars, and faster healing than regular (open) surgery.
Quicker Recovery: You can leave the hospital sooner and return to normal life faster.
Lower Infection Risk: Small cuts mean less chance of getting an infection.

